Some examples of the sesamoid bones are the patella bone in the knee or the pisiform bone of the carpus. Found within the bone, its function is to help maintain bone as living tissue.
Incredible What Are The Functions Of Bones With New Ideas, Bones are the anchor to which muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints attach. The different types of bone cells include the following:
 Overview Bone Functions Classification of Bones From studylib.net
Overview Bone Functions Classification of Bones From studylib.net
The bone system fulfills the following functions: This process of contract and release is repeated throughout the body. Type, structure, tissue, and cells. Examples of important protecting bones of the skeleton include the skull, spinal column and rib cage, which protect the brain, spinal cord, and heart and lungs.
Overview Bone Functions Classification of Bones The first mechanical function bones serve is to provide assistance in movement to the body.
The bones have more than just one function in the body. This is the process in which blood cell production begins in the yolk sac of the developing embryo, which is also referred to as hematopoiesis. The human skull consists of cranium and facial bones. Bones are the anchor to which muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints attach.
 Source: interactive-biology.com
Source: interactive-biology.com
They provide a safety environment for internal organs (brain. The bones serve as an internal shield, isolating and defending the vital organs. They act as levers, allowing the skeletal muscles to contract, which in turns moves the designated bone. Larger bones contain bone marrow, a spongy tissue inside the bones. Bones A Brief Review on its Functions, Types, Structure and.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Mandible is the only movable bone in the human skull. This is the process in which blood cell production begins in the yolk sac of the developing embryo, which is also referred to as hematopoiesis. The skeletal system as a whole serves five key functions: Skeletal muscles, which attach to bones by tendons, use bones as levers to move the body and its parts. PPT Bones in the human skeleton PowerPoint Presentation ID763141.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Type, structure, tissue, and cells. Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. The origin is the anchor, the bone that remains immobile while the muscle works. The skeletal system as a whole serves five key functions: Skeletal System Function and Components.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Bone is a connective tissue that performs several basic functions: Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. The bones are all joined together , articulated in a continuum, except for the hyoid bone, isolated in the lower part of the neck. A very large cell formed in bone marrow, its function is to absorb and remove unwanted tissue. Skeleton (pdf).
 Source: newhealthadvisor.com
Source: newhealthadvisor.com
Hemopoiesis, movement, support and protection, and storage of minerals and lipids. Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. The insertion is the bone that moves as the muscle works, which is one of the main functions of the skeleton. The human skeleton is made up of bones, these bones are composed of a mineral called calcium. Organs of Skeletal System and Their Functions New Health Advisor.
 Source: boneandspine.com
Source: boneandspine.com
What is the function of bone, cartilage and ligament ? As a result, we can walk, grasp objects, and breath. Found within the bone, its function is to form new bone tissue. Skeletal muscles, which attach to bones by tendons, use bones as levers to move the body and its parts. Different Types of Bones in Body and Their Function Bone and Spine.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones. The skeletal system as a whole serves five key functions: The insertion is the bone that moves as the muscle works, which is one of the main functions of the skeleton. They provide a safety environment for internal organs (brain. 9 best School images on Pinterest Bones, Human anatomy and Anatomy.
 Source: teachpe.com
Source: teachpe.com
The bones of the skeleton give the human body its defined shape and determine its posture. Some examples of the sesamoid bones are the patella bone in the knee or the pisiform bone of the carpus. There are five functions that the bones carry out in the body. The origin is the anchor, the bone that remains immobile while the muscle works. The Human Skeleton Bones, Structure & Function.
 Source: vdocuments.site
Source: vdocuments.site
Roles and functions of bones and muscles. Found within the bone, its function is to form new bone tissue. Skeletal muscles, which attach to bones by tendons, use bones as levers to move the body and its parts. The bones have more than just one function in the body. Musculoskeletal System. 2 Contents Introduction Functions of the.
 Source: exploringnature.org
Source: exploringnature.org
The main function of the sesamoid bone is to. A very large cell formed in bone marrow, its function is to absorb and remove unwanted tissue. Bones also maintain the blood calcium level by either absorbing calcium from blood or releasing calcium to the blood. What is the function of bone, cartilage and ligament ? Skeleton Structure and Function MiniPoster.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
They has the calcium which is main requirement for the impulse trans mission. Bones are the anchor to which muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints attach. Some examples of the sesamoid bones are the patella bone in the knee or the pisiform bone of the carpus. Red bone marrow present in the medullary cavity of spongy bone manufactures red blood cells. 5.2 functions of skeleton.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
As a result, we can walk, grasp objects, and breath. Bone is a connective tissue that performs several basic functions: Examples of important protecting bones of the skeleton include the skull, spinal column and rib cage, which protect the brain, spinal cord, and heart and lungs. The sesamoid bones are found at the end of long bones in the upper and lower limbs, where the tendons cross. Functions and types of bones.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. What is the function of bone, cartilage and ligament ? Some examples of the sesamoid bones are the patella bone in the knee or the pisiform bone of the carpus. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole. Overview Bone Functions Classification of Bones.
 Source: exploringnature.org
Source: exploringnature.org
The bones serve as an internal shield, isolating and defending the vital organs. The main function of the sesamoid bone is to. Examples of important protecting bones of the skeleton include the skull, spinal column and rib cage, which protect the brain, spinal cord, and heart and lungs. The fused bones of the skull protect the brain. Skeletal System Poster Downloadable Only.
 Source: thepeclassroom.com
Source: thepeclassroom.com
For example, the skull’s cranium houses the brain, and the ribs and sternum of the thoracic cage protect organs in the. The bone system fulfills the following functions: The main function of the sesamoid bone is to. They has the calcium which is main requirement for the impulse trans mission. Functions/Bones of the Body The PE Classroom.
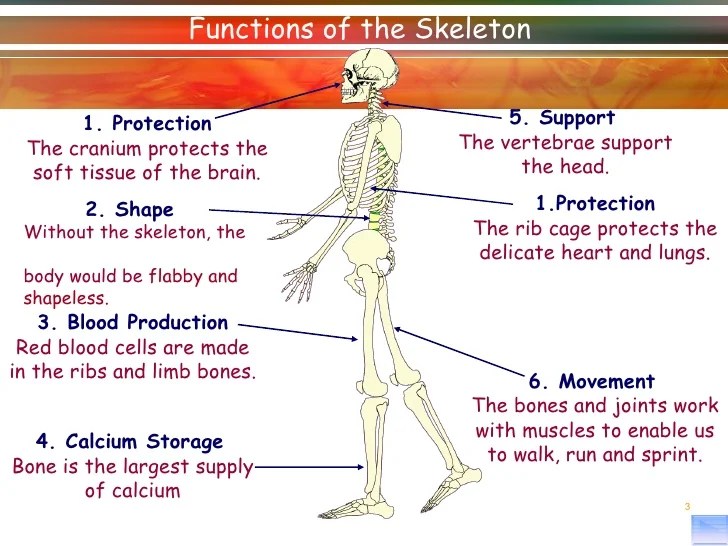 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Found within the bone, its function is to help maintain bone as living tissue. It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones. The function of the cranium is to protect the brain. Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. Principles of a+p 1112 session 3 function and classification of bon….
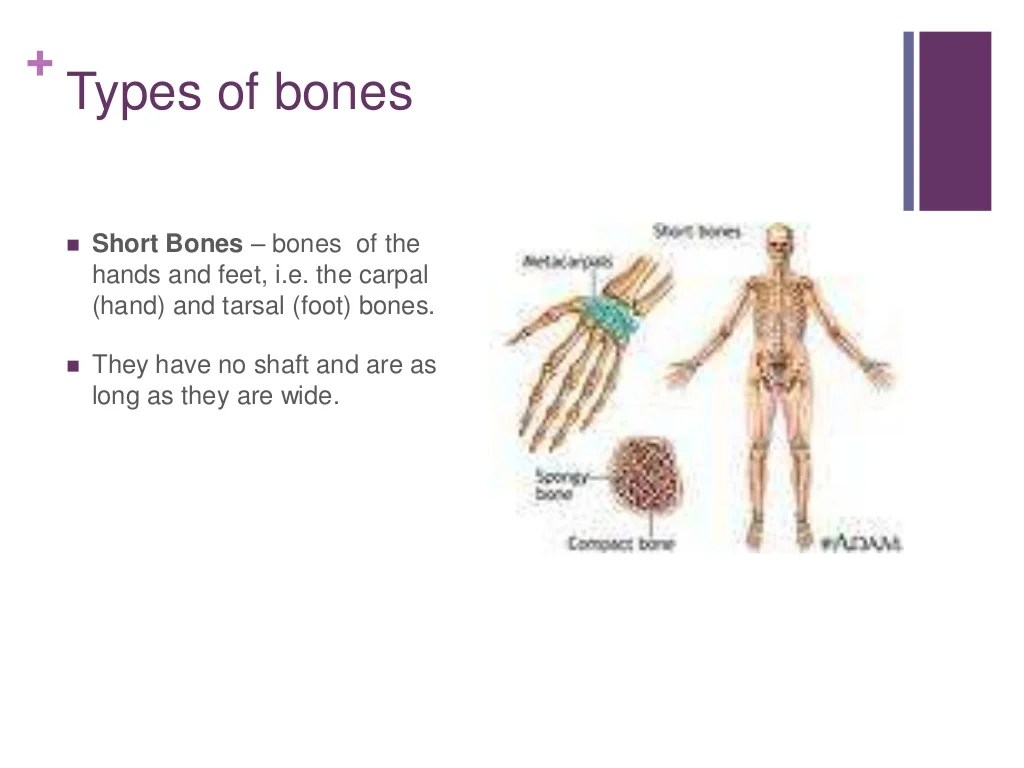 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Found within the bone, its function is to form new bone tissue. 2.they are the main place to attachment of muscles and few visceral organs. The bone system fulfills the following functions: The bones serve as an internal shield, isolating and defending the vital organs. Functions and types of bones.
 Source: semangakita.blogspot.com
Source: semangakita.blogspot.com
The hard outer layer of bones is composed of cortical bone, which is also called compact bone as it is much denser than cancellous bone. Hemopoiesis, movement, support and protection, and storage of minerals and lipids. Red bone marrow present in the medullary cavity of spongy bone manufactures red blood cells. Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. Desribe The Function Of The Bones Of The Head Neck And Shoulder / 14 2.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Larger bones contain bone marrow, a spongy tissue inside the bones. Roles and functions of bones and muscles. The fused bones of the skull protect the brain. Red bone marrow present in the medullary cavity of spongy bone manufactures red blood cells. Functions of Bone.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
The fused bones of the skull protect the brain. In skull.) (lungs and heart in rib cage) 4. The sesamoid bones are found at the end of long bones in the upper and lower limbs, where the tendons cross. The bones are all joined together , articulated in a continuum, except for the hyoid bone, isolated in the lower part of the neck. Skeletal System Function and Components.
 Source: medicinebtg.com
Source: medicinebtg.com
The function of the cranium is to protect the brain. This is the process in which blood cell production begins in the yolk sac of the developing embryo, which is also referred to as hematopoiesis. What is the function of bone, cartilage and ligament ? Larger bones contain bone marrow, a spongy tissue inside the bones. functions of bones the skeleton include they fulfill within body eg.
 Source: healthjade.net
Source: healthjade.net
Functions of the bones include support, protection, movement, storage, and. The bones have more than just one function in the body. So, for example, in the case of the biceps, the upper arm and shoulder are the origins (anchor) and the bones of the forearm are the insertion. There are two main types of marrow, red and yellow. Human Skeleton Skeletal System Function, Human Bones.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
They act as levers, allowing the skeletal muscles to contract, which in turns moves the designated bone. This process of contract and release is repeated throughout the body. The fused bones of the skull protect the brain. The function of the cranium is to protect the brain. Functions of the skeleton GCSE PE Revision YouTube.
 Source: skeletalsystemhfl.weebly.com
Source: skeletalsystemhfl.weebly.com
They provide rigidity and support to soft tissues, keeping everything in its respective place. Bones are the last part of the human body to break down. Examples of important protecting bones of the skeleton include the skull, spinal column and rib cage, which protect the brain, spinal cord, and heart and lungs. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole. functions Skeletal System.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Hemopoiesis, movement, support and protection, and storage of minerals and lipids. As a result, we can walk, grasp objects, and breath. 2.they are the main place to attachment of muscles and few visceral organs. There are five functions that the bones carry out in the body. Lesson 1 skeletal system.
The Fused Bones Of The Skull Protect The Brain.
Red bone marrow present in the medullary cavity of spongy bone manufactures red blood cells. Due to this mineral bone is a very hard substance, without the. The human skeleton is made up of bones, these bones are composed of a mineral called calcium. It facilitates bone's main functions—to support the whole.
This Process Of Contract And Release Is Repeated Throughout The Body.
The human skull consists of cranium and facial bones. So, for example, in the case of the biceps, the upper arm and shoulder are the origins (anchor) and the bones of the forearm are the insertion. Some examples of the sesamoid bones are the patella bone in the knee or the pisiform bone of the carpus. They provide rigidity and support to soft tissues, keeping everything in its respective place.
The Skeletal System As A Whole Serves Five Key Functions:
A very large cell formed in bone marrow, its function is to absorb and remove unwanted tissue. Functions of the bones include support, protection, movement, storage, and. This is the process in which blood cell production begins in the yolk sac of the developing embryo, which is also referred to as hematopoiesis. There are five functions that the bones carry out in the body.
Larger Bones Contain Bone Marrow, A Spongy Tissue Inside The Bones.
In skull.) (lungs and heart in rib cage) 4. The insertion is the bone that moves as the muscle works, which is one of the main functions of the skeleton. The different types of bone cells include the following: It forms the hard exterior (cortex) of bones.







