Tilt angle is measured perpendicular to line of. The orbital plane is defined by two parameters, inclination and longitude of the ascending node.
Simple Define The Orbital Plane With Creative Ideas, An object in an orbit is called a satellite. Tilt angle is measured perpendicular to.
 Earth science GEOPHYSICS From gpsurya.blogspot.com
Earth science GEOPHYSICS From gpsurya.blogspot.com
1 n (astronomy) the plane on which a body is orbiting type of: Isotropic distributions will uniformly cover the unit sphere. All of the planets, comets, and asteroids in the solar system are in orbit around the sun. The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies.
Earth science GEOPHYSICS The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit lies.
Information and translations of orbital plane in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of. It passes through the center of force. The two vectors r and r ˙ define a plane called the orbital plane.
 Source: pistonheads.com
Source: pistonheads.com
Orbital plane and kepler’s second law. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit lies. An object in an orbit is called a satellite. For d orbital the value of l=2 thus the minimum value of principal quantum number n is 3. question probably missing something obvious Page 1.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
1 n (astronomy) the plane on which a body is orbiting type of: The reference plane for the solar system is usually the earth's orbital plane. They do not orbit at all angles, as below. The unit vector normal to the plane is: Angular orbital elements referred to in this study. Inclination (i) is.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
The axis of the earth (an imaginary line) makes an angle of 661 2∘ with its orbital plane. 1 n (astronomy) the plane on which a body is orbiting type of: The orbital plane is defined by two parameters, inclination and longitude of the ascending node. Inclination (i) — vertical tilt of the ellipse with respect to the reference plane, measured at the ascending node (where the orbit passes upward through the reference plane, the green angle i in the diagram). Why is Pluto's orbit different compared to other Socratic.
 Source: archive.eetasia.com
Source: archive.eetasia.com
The unit vector normal to the plane is: The two vectors r and r ˙ define a plane called the orbital plane. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit lies. What is the orbital plane? Fly me to the Moon (Part 4) Programmer's Toolbox EE Times Asia.
 Source: space.stackexchange.com
Source: space.stackexchange.com
The plane formed by the orbit is known as the orbital plane. This defines the ecliptic, the path on the celestial sphere that the sun appears to follow over a year. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) and of an orbiting celestial body at two different times/points of its orbit. The d orbital is cloverleaf or two dumbbells in a plane. orbital mechanics Solar system galactic velocity vector relative to.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A satellite can be natural, like earth or the moon. Orbital plane definition at dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. All of those orbits line up with each other making a kind of flat disk called the orbital plane. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit lies. An illustration of the Moon's orbital plane around the Earth and.
 Source: gurukulkendra.com
Source: gurukulkendra.com
An orbit is a regular, repeating path that one object in space takes around another one. The orbital surface of the maxilla, lying perpendicular to the orbitomeatal plane at the orbitale. The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of. 1 n (astronomy) the plane on which a body is orbiting type of: Orbital plane Gurukul Kendra.
 Source: geography.name
Source: geography.name
A standard craniometric reference plane passing through the right and left porion and the left orbitale; There are five orientations for a d orbital, as shown here. Depending on the relative sizes of the stars, the orbital inclination over which eclipses can occur is considerable, but in general only a small fraction of the known binary systems will be seen to undergo eclipses. It passes through the center of force. The Earth's Revolution around the Sun.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
[omega] and i, which define the orientation of the orbital plane in the reference system used. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit lies. H ^ = h h. The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. You Are Observing A Satellite In An Inclined Orbit….
 Source: nsta.org
Source: nsta.org
The orbital plane is defined in relation to a reference plane by two. A common example would be: The d orbital is cloverleaf or two dumbbells in a plane. There are five orientations for a d orbital, as shown here. The Moon’s Inclined Orbital Plane NSTA.
 Source: alsadeemastronomy.ae
Source: alsadeemastronomy.ae
1 n (astronomy) the plane on which a body is orbiting type of: The orbital plane is defined by two parameters, inclination (i) and longitude of the ascending node (ω). A common example would be: Contribution to the theory of the determination of the orbital elements of solar. PARTIAL LUNAR ECLIPSE 2017 Al Sadeem Astronomy.
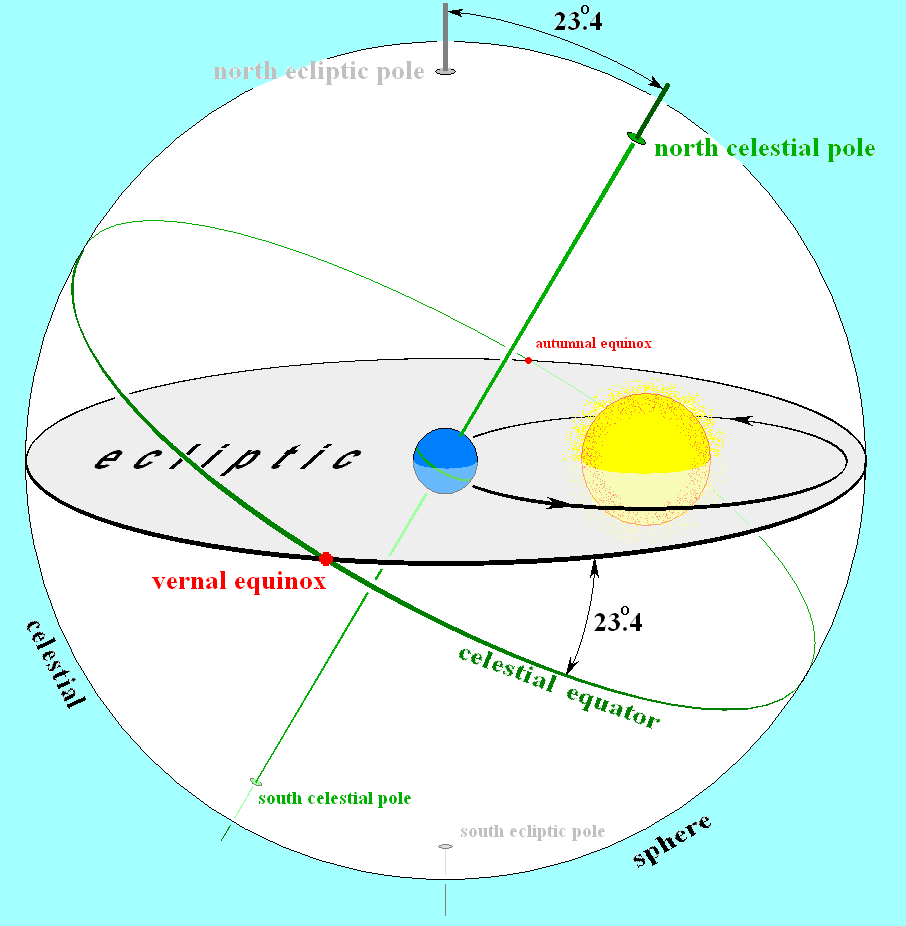
A common example would be: The orbital plane is defined in relation to a reference plane by two. Depending on the relative sizes of the stars, the orbital inclination over which eclipses can occur is considerable, but in general only a small fraction of the known binary systems will be seen to undergo eclipses. The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Coordinate Systems in KStars.
 Source: spaceplace.nasa.gov
Source: spaceplace.nasa.gov
Planets, comets, asteroids and other objects in. The d orbital is cloverleaf or two dumbbells in a plane. An object in an orbit is called a satellite. The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of. All About Pluto NASA Space Place.
 Source: earthsky.org
Source: earthsky.org
What is the orbital plane? They do not orbit at all angles, as below. 1 n (astronomy) the plane on which a body is orbiting type of: Due to the earth's spherical shape, only one part of it receives sunlight while the other half remains dark. Do all orbit in a flat plane around their suns? Space EarthSky.

The orbital plane is defined by two parameters, inclination (i) and longitude of the ascending node (ω). The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of. A common example would be: For d orbital the value of l=2 thus the minimum value of principal quantum number n is 3. Does a satellite's orbit always intersect the equator? Are there any.
 Source: gpsurya.blogspot.com
Source: gpsurya.blogspot.com
The plane which contains the orbit of a body or particle in a central force field; The orbital plane is defined in relation to a reference plane by two parameters: Inclination (i) — vertical tilt of the ellipse with respect to the reference plane, measured at the ascending node (where the orbit passes upward through the reference plane, the green angle i in the diagram). The orbital plane is defined in relation to a reference plane by two. Earth science GEOPHYSICS.
 Source: nationalgeographic.org
Source: nationalgeographic.org
For d orbital the value of l=2 thus the minimum value of principal quantum number n is 3. A common example would be: Tilt angle is measured perpendicular to line of. The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of the orbiting object at some later time. Orbital Plane National Geographic Society.
 Source: worldbuilding.stackexchange.com
Source: worldbuilding.stackexchange.com
Depending on the relative sizes of the stars, the orbital inclination over which eclipses can occur is considerable, but in general only a small fraction of the known binary systems will be seen to undergo eclipses. Orbital plane and kepler’s second law. The reference plane for the solar system is usually the earth's orbital plane. A common example would be: science based Can I produce a true 3D orbit? Worldbuilding Stack.
 Source: nsta.org
Source: nsta.org
Two elements define the orientation of the orbital plane in which the ellipse is embedded: Orbital plane definition at dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Isotropic distributions will uniformly cover the unit sphere. Depending on the relative sizes of the stars, the orbital inclination over which eclipses can occur is considerable, but in general only a small fraction of the known binary systems will be seen to undergo eclipses. The Moon’s Inclined Orbital Plane NSTA.
 Source: astronomy.stackexchange.com
Source: astronomy.stackexchange.com
A standard craniometric reference plane passing through the right and left porion and the left orbitale; The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of the orbiting object at some later time. The normal points to a single point on a unit sphere. Tilt angle is measured perpendicular to line of. orbital mechanics J2 perturbations and orbits Astronomy Stack Exchange.
 Source: cnyo.org
Source: cnyo.org
The d orbital is cloverleaf or two dumbbells in a plane. The orbital plane of eclipsing stars lies perpendicular to the plane of the sky. The orbital plane is defined in relation to a reference plane by two parameters: A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) and of an orbiting celestial body at two different times/points of its orbit. orbital plane CNY Observers & Observing.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The orbital plane is defined by two parameters, inclination and longitude of the ascending node. The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of the orbiting object at some later time. This defines the ecliptic, the path on the celestial sphere that the sun appears to follow over a year. What is the orbital plane? Overview of Our System Astronomy.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Drawn on the profile radiograph or photograph from the superior margin of the acoustic meatus to the orbitale. Isotropic distributions will uniformly cover the unit sphere. A satellite can be natural, like earth or the moon. H ^ = h h. 4 Three dimensional figure of orbital plane of binary stars. z is the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The center of the heavier object, the center of the orbiting object and the center of the orbiting object at some later time. [omega] and i, which define the orientation of the orbital plane in the reference system used. The axis of the earth (an imaginary line) makes an angle of 661 2∘ with its orbital plane. Two elements define the orientation of the orbital plane in which the ellipse is embedded: Orientation of the Earth in space the plane defined by the Earth's.
 Source: qrg.northwestern.edu
Tilt angle is measured perpendicular to line of. The orbital plane of eclipsing stars lies perpendicular to the plane of the sky. All of the planets, comets, and asteroids in the solar system are in orbit around the sun. It passes through the center of force. What is the orbital plane?.
The Orbital Plane Is Defined In Relation To A Reference Plane By Two.
The orbital plane is defined by two parameters, inclination (i) and longitude of the ascending node (ω). Planets, comets, asteroids and other objects in. Isotropic distributions will uniformly cover the unit sphere. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit lies.
The Planets All Orbit On Or Near One Plane In Space Like The Picture Above.
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. The plane which contains the orbit of a body or particle in a central force field; Information and translations of orbital plane in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. Since the angular momentum is constant for all time, it.
In The Exercise Below, If We Randomly Draw Orbital Plane Orientations Using Either An Uniform Or Sine.
The reference plane for the solar system is usually the earth's orbital plane. A common example would be: H ^ = h h. The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies.
For Example, Suppose A Planet Is Orbiting Around A Star In An Elliptical Orbit.
The plane formed by the orbit is known as the orbital plane. Where h is the magnitude of the specific angular momentum. An object in an orbit is called a satellite. Any line joining two points on a plane.







