It is present in metals and defines all their physical properties that characterize them as hard, ductile, malleable materials and good conductors of heat and electricity. Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking.
Step By Step What Makes A Metallic Bond With Creative Ideas, First, as the name implies, this type of bonding is found in metals and metal alloys. Bonding between metals and nonmetals.
 PPT METALLIC BOND PowerPoint Presentation ID4554784 From slideserve.com
PPT METALLIC BOND PowerPoint Presentation ID4554784 From slideserve.com
The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. The ionic bond is formed between cation and anion by the electrostatic force of attraction. The remaining ions also have twice. Brass is a metallic compound (having a metallic bond).
PPT METALLIC BOND PowerPoint Presentation ID4554784 The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements.
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The ionic bond is formed between cation and anion by the electrostatic force of attraction. The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. Malleability ductility high melting and boiling point high electrical and thermal conductivity metallic lustre The free electrons shield the positively charged ion cores from the. Metallic Bonding YouTube.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Instead, many electrons (roughly one for each atom) are more or less free to move throughout the metal, so that each electron can interact with many of the fixed atoms. A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. Mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper. PPT Metallic bonding and properties PowerPoint Presentation, free.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. The metallic bond is the one that holds the atoms of the metallic elements tightly together. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement. PPT Metallic Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID711524.
 Source: sansona.github.io
Source: sansona.github.io
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper. But in metallic bonds, the electrostatic force of attraction is between the kernel and delocalized electron. Attractive Forces and Bonds.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. Of all the chemical bonds, the metallic bond is the only one where the electrons. The structure of a metallic bond is quite different from covalent and ionic bonds. In a metallic bond, the valence electrons are delocalised, meaning that an atom’s electrons do not stay around that one nucleus.in a metallic bond, the positive atomic nuclei (sometimes called the “atomic kernels”) are surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons. PPT 4.4 Metallic bonding PowerPoint Presentation ID400526.

Because metals are solid,the atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement.because they are so close to each other,the valence electrons tend to move away from their atoms.a ‘sea’ of free,delocalised electrons is formed surrounding a lattice. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. This is a metallic bond example. Metallic Bonding Metals Ductility.
 Source: embibe.com
Source: embibe.com
Pure gallium creates covalent bonds between pairs of atoms that are connected to. Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement. A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. They are so close to each other so valence electrons can be moved away from. Metallic Bonding Definition, Properties, Examples, Diagram.
 Source: microblife.in
Source: microblife.in
Here (a) is brittle, (b) is partially ductile and (c) is completely ductile in nature. The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. Because metals are solid,the atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement.because they are so close to each other,the valence electrons tend to move away from their atoms.a ‘sea’ of free,delocalised electrons is formed surrounding a lattice. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. What is Covalent Bond? Micro B Life.
 Source: obfuscata.com
Source: obfuscata.com
The ionic bond is formed between cation and anion by the electrostatic force of attraction. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. Where other bonds are, in a way, an arrangement with a very specific set of atoms to share those electrons, metal atoms sort of shed the outer coating of. This is a metallic bond example. Examples for Metallic Bonds.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
There are “primary bonds” or “strong bonds. Metallic bonds are formed when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. Therefore, an ionic bond is stronger than a metallic bond. A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. PPT METALLIC BOND PowerPoint Presentation ID4554784.

Metallic bonds are formed when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Metallic bonds are not discrete directional bonds between specific atoms, so it often makes sense to talk about metallic “bonding” rather than individual bonds. Other sorts of chemical bonds can be formed between the atoms of metals, even if they are pure. What is metallic bond? Quora.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In a metallic bond, the valence electrons are delocalised, meaning that an atom’s electrons do not stay around that one nucleus.in a metallic bond, the positive atomic nuclei (sometimes called the “atomic kernels”) are surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons. Therefore, an ionic bond is stronger than a metallic bond. But what are the characteristics of this kind of bonding? The metallic bond is the one that holds the atoms of the metallic elements tightly together. Bonding & Properties Metallic Bonding YouTube.
 Source: obfuscata.com
Source: obfuscata.com
In a metallic bond, the valence electrons are delocalised, meaning that an atom’s electrons do not stay around that one nucleus.in a metallic bond, the positive atomic nuclei (sometimes called the “atomic kernels”) are surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability. Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking. The positively charged sodium metal ions and negatively charged electrons get bonded together forming metallic bonds. Strength of Metallic Bonds.
 Source: robhosking.com
Source: robhosking.com
The free electrons shield the positively charged ion cores from the. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. In ionic bond and metallic bond, which is stronger? Of all the chemical bonds, the metallic bond is the only one where the electrons. 12+ Metallic Bonding Diagram Robhosking Diagram.
 Source: obfuscata.com
Source: obfuscata.com
Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement. Metallic bonds are formed when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; This is a metallic bond example. Examples for Metallic Bonds.
 Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk
Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons. Pure gallium creates covalent bonds between pairs of atoms that are connected to. The structure of a metallic bond is quite different from covalent and ionic bonds. The brain is designed in such a way that it is cleared of. Metallic bonding teaching resources the science teacher.
 Source: en.ppt-online.org
Source: en.ppt-online.org
Therefore, an ionic bond is stronger than a metallic bond. The ionic bond is formed between cation and anion by the electrostatic force of attraction. In a sample of metal, the valence electrons detach from the. In a metallic bond, the valence electrons are delocalised, meaning that an atom’s electrons do not stay around that one nucleus.in a metallic bond, the positive atomic nuclei (sometimes called the “atomic kernels”) are surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons. Metals online presentation.
 Source: embibe.com
Source: embibe.com
The properties of metals that are a consequence of metallic bonding include: Other sorts of chemical bonds can be formed between the atoms of metals, even if they are pure. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; Of all the chemical bonds, the metallic bond is the only one where the electrons. Metallic Bonding Definition, Properties, Examples, Diagram.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
If you work through the same argument with magnesium, you end up with stronger bonds and so a higher melting point. Sap‑3 (eu), sap‑3.a (lo), sap‑3.a.5 (ek) transcript. Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement. Where other bonds are, in a way, an arrangement with a very specific set of atoms to share those electrons, metal atoms sort of shed the outer coating of. metallic bond Properties, Examples, & Explanation Britannica.
 Source: expii.com
Source: expii.com
The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability. The remaining ions also have twice. A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. Mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper. Metallic Bond — Formation & Compounds Expii.
 Source: mydigitalkemistry.com
Source: mydigitalkemistry.com
But what are the characteristics of this kind of bonding? As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of. A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. The metallic bonding (electron sea model) can explain the physical properties of metals. Metallic Bond Definition, Examples ,Properties 3d Animation Best.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The two elements that make it up are both metals; Malleability ductility high melting and boiling point high electrical and thermal conductivity metallic lustre The ionic bond is formed between cation and anion by the electrostatic force of attraction. Of all the chemical bonds, the metallic bond is the only one where the electrons. Metallic bonding.
 Source: sciencenotes.org
Source: sciencenotes.org
The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; In metals, each atom has 8 or 12 neighboring atoms surrounding them and the valence electrons in the metal atoms are less than four. Other sorts of chemical bonds can be formed between the atoms of metals, even if they are pure. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. Metallic Bonding Definition and Properties.
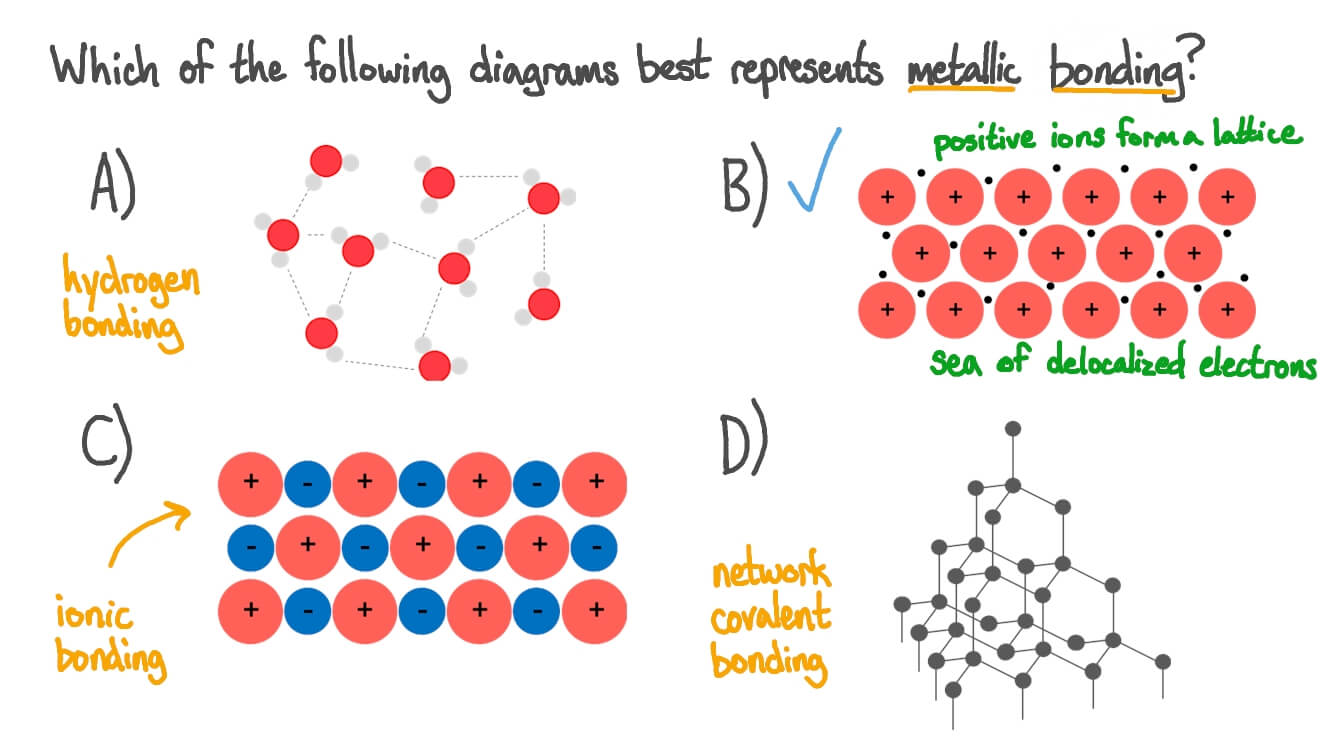 Source: nagwa.com
Source: nagwa.com
Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Magnesium has the outer electronic structure 3s 2. The nature of the metallic bond. The free electrons shield the positively charged ion cores from the. Question Video Identifying the Structure of a Metallic Bond Nagwa.
 Source: studyrocket.co.uk
Source: studyrocket.co.uk
The free electrons shield the positively charged ion cores from the. In most cases, the outermost electron shell of each of the metal atoms overlaps with a large number of neighbouring atoms. But in metallic bonds, the electrostatic force of attraction is between the kernel and delocalized electron. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Metallic Bonding GCSE Chemistry Science) AQA Revision.
Metallic Bonds Are Formed When The Charge Is Spread Over A Larger Distance As Compared To The Size Of Single Atoms In Solids.
Of all the chemical bonds, the metallic bond is the only one where the electrons. Sap‑3 (eu), sap‑3.a (lo), sap‑3.a.5 (ek) transcript. Here (a) is brittle, (b) is partially ductile and (c) is completely ductile in nature. In a sample of metal, the valence electrons detach from the.
Because Metals Are Solid, Their Atoms Are Tightly Packed In A Regular Arrangement.
Because metals are solid,the atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement.because they are so close to each other,the valence electrons tend to move away from their atoms.a ‘sea’ of free,delocalised electrons is formed surrounding a lattice. The positively charged sodium metal ions and negatively charged electrons get bonded together forming metallic bonds. Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. It can be defined as the electrostatic force of.
In A Metallic Bond, The Valence Electrons Are Delocalised, Meaning That An Atom’s Electrons Do Not Stay Around That One Nucleus.in A Metallic Bond, The Positive Atomic Nuclei (Sometimes Called The “Atomic Kernels”) Are Surrounded By A Sea Of Delocalised Electrons.
Therefore, an ionic bond is stronger than a metallic bond. Metallic bonds are not discrete directional bonds between specific atoms, so it often makes sense to talk about metallic “bonding” rather than individual bonds. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding formed in the metals.
There Are “Primary Bonds” Or “Strong Bonds.
In metals, each atom has 8 or 12 neighboring atoms surrounding them and the valence electrons in the metal atoms are less than four. Three different types of primary or chemical bond are found in solids. Where other bonds are, in a way, an arrangement with a very specific set of atoms to share those electrons, metal atoms sort of shed the outer coating of. As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of.







